In 1553 the French naturalist Pierre Belon published, in his book on aquatic animals De Aquatilibus, the here shown depiction of what at first glance appears to be a frightening sea-monster. Belon’s discussion of this animal is serious and detailed. This animal catches it’s prey by leaping up from the water, he writes, and he advises his readers not to eat it. It has a foul taste and smell, he explains, and can upset the stomach.
Pierre Belon. De aquatilibus. Paris, Charles Estienne, 1553. Library of the United States Department of Agriculture, Cambridge (Mass.).
What Belon fails to mention, and most likely did not know, is that this animal is in fact a European eagle ray which has been cut and twisted before being dried, in order to make it look like a monster. The distorted snout and twisted body are sure sights of human interference, and in fact such distorted rays were created on a large scale across Europe at this time. In the sixteenth century monsters were very much ‘in fashion’, and this widespread interest made it a lucrative business to create objects that could reasonably pass as monstrous creatures.

The European eagle ray. Image by Patrik Neckman from Stockholm, Sweden (Majestic ray) [CC BY-SA 2.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0)%5D, via Wikimedia Commons
Five years later, in 1558, the less gullible Conrad Gessner included such a creation in his Historiae Animalium and explained to his readers exactly how these were made. “Apothecaries and others”, he writes, “let the body of the ray dry and twist the skeleton, making the animal look like a winged serpent or a dragon. They bend the body and alter the shape of the head and mouth, and cut other parts off. The back and bottom part of the animal is tampered with and turned upright, making the animal look like it has wings”
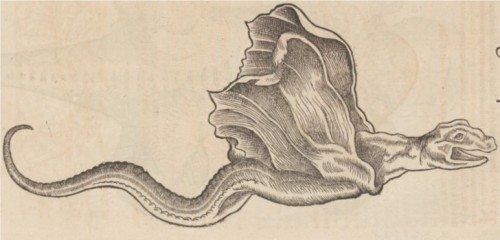
Conrad Gesner. Historiae animalium liber IIII. Zurich, Christoph Froschauer, 1558. SUB Göttingen HSD
Gessner admits that he also initially did not know the animal was a fake. The depiction was sent to him by an apothecary, who did not disclose this. Eventually however, he figured it out, and he strongly disapproved of the practice. He explains that he discloses how these creatures are made in order to warn his readers about these fakes, and about the fraudulent people who exhibit them and charge others money to see them. This needs to be explained, he writes, as “ordinary people are very much impressed with these things”.

Part of Gessner’s description of the dried ray. SUB Göttingen HSD
Rays and skates are in fact extremely suitable to make creations such as these. These fish already have a suggestive appearance, their underside looks to us as if we see a semi-human face, the nostrils looking like a pair of eyes. In addition, they can be easily manipulated, by curling the side fins over the back, twisting the tail into strange positions, and using string tied behind the head to create a neck. Finally, rays and skates can be easily dried in the sun, and shrink when this is done, resulting in an even more twisted and monstrous appearance.

Image by Adamantiaf. (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0)%5D, via Wikimedia Commons
In 1613 Gessner’s acquaintance and correspondent Ulysse Aldrovandi published a range of depictions of such monstrous dried rays, or jenny hanivers as they are nowadays called, in his De piscibus. The origin of the term jenny haniver may lie in the French phrase jeune d’Anvers, Antwerp having been a centre of production for these things.
An ardent collector of all sorts of naturalia Aldrovandi may well have seen and handled all the jenny hanivers he included in his book. It is known he owned several of them. The here shown depictions shows one which resembles a flying dragon which looks like it is mid-flight. Much like Gessner, Aldrovandi clearly indicates that such creatures are not real.
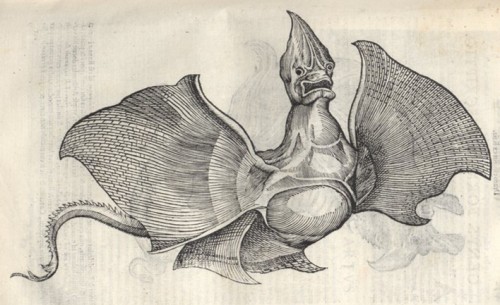
Ulysse Aldrovandi. De piscibus. Bologna, Baptiste Bellagamba, 1613. Université Louis Pasteur from University of Strasbourg.
So does this mean that once the word was out naturalists were more sceptical about reports they received about strange creatures from the sea? Perhaps that is an overstatement. In spite of his critical description of the above shown specimen, Gessner also shows Belon’s jenny haniver in his Historiae Animalium and copies Belon’s description of it almost word for word, without any of the criticism voiced in his description of the other jenny haniver. One possible explanation for this is that it mattered to Gessner whether or not information came from what he perceived as a reliable source. An esteemed naturalist such as Pierre Belon was certainly that.

Conrad Gesner. Historiae animalium liber IIII. Zurich, Christoph Froschauer, 1558. SUB Göttingen HSD
On top of this, just because something seems unlikely does not necessarily mean it isn’t true. As Gessner writes referring to other monstrous creatures, such as the sea-monk and the sea-satyr: some creatures have been reported either so often or by such reliable sources that he cannot exclude the possibility that they exist.
Further reading:
Pierre Belon. De aquatilibus. Paris, Charles Estienne, 1553.
Conrad Gesner. Historiae animalium liber IIII. Zurich, Christoph Froschauer, 1558.
Ulysse Aldrovandi. De piscibus. Bologna, Baptiste Bellagamba, 1613.
Sophia Hendrikx. Het eerste en misschien ook wel het kleinste en mooiste boek over waterdieren. In: Hans Mulder en Erik Zevenhuizen (Red.), De natuur op papier. 175 jaar Artis Bibliotheek. Amsterdam, Athenaeum-Polak & Van Gennep, 2013.
Peter Dance. Animal frauds and fakes. Maidenhead, Berkshire, Sampson Low, 1976.
© Sophia Hendrikx and Fishtories, 2016. Unauthorised use and/or duplication of this material without express and written permission from this site’s author and/or owner is strictly prohibited. Excerpts and links may be used, provided that full and clear credit is given to Sophia Hendrikx and Fishtories with appropriate and specific direction to the original content.
This blogpost also appeared on The Leiden Arts and Society Blog.

Hello Sophia,
I liked your text and took the freedom to refer to it on my website “Fish in time and history”.
I am looking forward to read more of your research.
Kind regards, Ulrike
LikeLike
Well done artcile that. I’ll make sure to use it wisely.
LikeLike
[…] year and a half ago in a blogpost on sixteenth century Monstreous Rays and Fraudulent Apothecaries, I referred to a description of a sea-creature resembling a winged snake or a dragon from Conrad […]
LikeLike